Definitive Guide to Change Management & Change Control for Medical Devices

In an industry that is ever-evolving, change is inevitable.
How medical device companies manage changes will undoubtedly have a huge impact on their business, including their internal processes and the products that they design, develop, manufacture, and distribute into the market. Ultimately, how companies handle and manage changes will impact patient lives.
As needs for changes arise, you’ll need to properly manage any changes made to ensure everything is accounted for in your quality management system and the resulting documentation and records.
This guide will detail the change management best practices that medical device companies need to understand and follow when making changes to documents, products, processes, and more.
Let’s begin by taking a look at what change management is and how change should be managed within the quality ecosystem at a medical device company.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
Use Cases of Change |
| Common Change Management Challenges |
|
Change Control Process |
|
QMS Requirements for Change Management |
|
Change Assessment |
|
Tasks and Actions |
|
Documenting Decisions and Supporting Evidence |
|
Pre-Market Changes |
|
Post-Market Changes |
|
Process Risk Assessment |
![DGCM_1]() What Is Change Management?
What Is Change Management?
Change management refers to the way a company manages modifications to products and processes within their medical device business. Change can come about for a number of reasons, and we refer to these as triggers for change.
Many events can trigger a change throughout the lifecycle of a product or organizations, including:
-
New or modified products, as well as any subsequent change to those products
-
New or modified processes for how you conduct business as you right-size and grow your QMS
-
New or modified controlled documents, such as templates, work orders, forms, etc., as well as any subsequent revisions made to those documents
New products, processes, or controlled documents all require change management practices be put in place. A change can involve modifications to records and procedures in your design controls, or your device master record (DMR). You might find yourself needing to do additional validation on a device, or maybe you are changing suppliers, which requires changes to associated documents and procedures.
Use Cases of Change
Changes could also be driven by new regulations that will require updates to specific processes and procedures. Or maybe you have identified opportunities for improvements to your products and processes to focus on “true quality” initiatives. While these are all somewhat predictable triggers, there will also be unexpected situations during the post-market surveillance that may prompt the need for change.
Let’s say a CAPA investigation reveals that devices are being damaged in transit due to a combination of the packaging design and failure to account for extreme temperature conditions during shipping - this could trigger a change to the devices packaging design or updated requirements when handling the devices during shipment.
Repeat quality issues with a partner supplying a critical component for your device could introduce business risk associated with that supplier. This could trigger a change wherein your team elects to qualify a new supplier for that component.
Post-market design changes can also occur based on feedback or complaints from end users, or ongoing research into a product after launch. A physician could recommend that a medical instrument be easier to grip to prevent it slipping during use. Perhaps your team will go through the change management process and elect to install an overmolded elastometer to improve the physicians ability to grip the device, and this is an example of a design change.
Common Change Management Challenges
Lack of visibility
Identifying all of the documents impacted by a proposed change order is a tedious and error-prone process. I need an easy way to find all the information that may be impacted by a change, so I don’t miss anything
It requires either encyclopedic knowledge of the quality management system, or a labor-intensive search through a large number of documents to find connections.
Stuck waiting - working reactively
Feels like we are starting over every time. We can’t do paperwork for its own sake. I don’t want to spend the time documenting, linking, and reviewing documents. I need to know if something has already been done.
We are losing money that we did not budget for from the hidden costs of redoing things. Recalls can cost millions and the safety of the product could be at risk.
Increased risk
I am under pressure to balance speed, high quality and lower costs. We cannot risk the safety of our products because we missed something in the change process.
This often results in missed documents, requiring multiple change orders to be processed, or even worse, inconsistent and incomplete changes to be made to processes and product lines.
Change Control Process
While the factors that can trigger the need for a change can vary, the change control process will often times involve similar steps.
To implement any change, you will need to do the following:
-
Describe the change you’re making.
-
Justify the reason for the change.
-
Identify what business outcomes will be affected.
-
Identify the people who need to be involved to assess and implement the change.
Every step in effectively managing change begins and ends with communication. For example, you may choose to change a material used in the product, or the logo on your packaging. To make sure the change is managed efficiently and accounts for both stakeholder and compliance impact, you must facilitate clear communication between internal and external stakeholders being impacted by the change.
Let’s use our checklist to go through the recommended process for a process change.
Let’s say a CAPA investigation reveals that devices are being damaged in transit due to a combination of the packaging design and failure to account for temperature conditions when shipping. This investigation may trigger a change to the shipping requirements and packaging design.
To describe the change, you’ll need to update your packaging specifications and requirements. When you define the reason for the change, you’ll cite the benefits — the proposed packaging is more durable and resilient to the temperature during shipping.
To identify the business outcome, a brainstorming session would be the best practice. This would involve people from multiple departments putting their heads together to hypothesize the possible outcomes.
To do this, you’ll need to identify the people who need to be involved. In the case of our change, this would potentially involve graphic design, packaging, marketing/sales, and regulatory affairs at the very least. You must update any documents and work instructions associated with the packaging, and these will be reviewed by the relevant people within your organization.
That’s a very broad view of what a change management incident might look like. Let’s dig a little deeper and take a look at the more granular processes and factors behind implementing and managing a change.
QMS Requirements for Change Management
As with product development in general, change management requires a high degree of traceability within your quality management system (QMS). That means clear, traceable relationships between the different stages of the change management process documented in your QMS. If this is done correctly, you will be able to see how each decision you make in change management leads into the next, carefully documenting each step of the process in chronological order.
Maintaining traceability while managing change initiatives will allow you to monitor any changes to documents, processes, or products. Again, various departments and functions within your business will be reviewing your changes, so being able to easily share key documents and track who’s reviewing and approving which documents included in the scope of the change is important.
There are different standards and regulations in place that outline the QMS requirements that will dictate your change management procedures.
(a) FDA Regulation
Under the FDA regulation, design change management is covered in FDA 21 CFR 820.30(i), albeit quite briefly:
Design changes: Each manufacturer shall establish and maintain procedures for the identification, documentation, validation or where appropriate verification, review, and approval of design changes before their implementation.
The regulation doesn’t go into much detail here, so it’s up to the manufacturer to interpret what design changes mean to you and to consider the best approach for your specific plans to implement change. A good rule of thumb to consider when determining if the proposed change is a design change is to answer the following questions.
- Does the change impact the device “form”?
- Does the change impact the device “fit”?
- Does the change impact the device “function”?
At the very least a “yes” to any of the above indicates a design change to the device.
The quality system regulation does provide us with the information needed to evaluate and implement design changes, and a design review is always a good way to determine impact on design controls and risk management, including whether verification and validation are necessary. A documented design review demonstrates that design controls or risk factors are adequately assessed, addressed, and updated in the product’s design history file (DHF).
CFR 820.40(b) outlines the requirements for change management in relation to document control:
Document changes: Changes to documents shall be reviewed and approved by an individual(s) in the same function or organization that performed the original review and approval, unless specifically designated otherwise. Approved changes shall be communicated to the appropriate personnel in a timely manner. Each manufacturer shall maintain records of changes to documents. Change records shall include a description of the change, identification of the affected documents, the signature of the approving individual(s), the approval date, and when the change becomes effective.
While there’s still room for interpretation, this clause is a little more prescriptive and makes it clear that device manufacturers must identify a designated individual(s) to review and approve any change that occurs and must inform them in a “timely manner.”
In addition, we are given a specific list of information that must be contained in the change records within the QMS.
(b) ISO Standard
Regulatory bodies like Health Canada and the European Commission, among others around the world, rely on ISO 13485:2016 for document and design change management.
The ISO standard goes into a little more detail with regards to change than the FDA regulation, mentioning change over 30 times throughout the 2016 standard. Having said that, the requirements for change from FDA and ISO are very similar to one another, requiring detailed documentation and traceability of every change within a QMS.
There is however an entire section of the ISO 13485 standard, section 4.1.4, that is dedicated specifically to managing changes to an organization’s QMS processes and complying with regulatory change control requirements.
The steps in the ISO standard are more or less the same as the FDA requirements. Change management is a very broad process, and, throughout this guide, we’ll continue to break down the individual parts of the process as a whole, in order to help you learn how to implement changes and record them in the QMS of your own company.
Greenlight Guru’s QMS software is purpose-built to establish and maintain full traceability throughout the lifecycle of your medical device, making processes around change, seamless and easy to manage.
The change management functionality of Greenlight Guru's QMS software allows users to understand and manage the impact of any change made by your organization and enables users to accurately and easily describe change management processes internally and to potential auditors/inspectors.
![DGCM_2]() Controlling and Managing Change
Controlling and Managing Change
Your change management processes should be defined and established in procedures and possibly detailed work instructions. These procedures shall describe evaluating your change, identifying what action(s) needs to be taken, and thoroughly document everything that is affected. Here’s a breakdown of how a change management process should flow.
Change Assessment
The change management process should begin with an assessment. To even consider implementing a change, you need to have an understanding of how it will impact your products, processes, and your company — even small changes need some form of assessment before being put into place.
Here are the six assessment criteria you’ll need to consider in the change management process:
-
Scope: The scope of a change will determine how much time and money will be required. Brainstorm with select individuals in your organization whom you feel should be included in these discussions. This will help you get a sense of how “big” or “small” your change is. Take your time here, as this will set the foundation for your change management activities and may even shift your regulatory strategy if you determine that a regulatory submission will be required for your change.
-
Description: This is where the communication aspect of change management comes into play. Anyone who has worked on design controls will know the value of clear communication. Avoid ambiguity when describing procedures, processes, and product specifications. Your proposed change, along with how any internal procedures or documents will be altered, will need to be described in no uncertain terms.
- Justification: You need to be able to explain, internally and externally, your reasons for making a change. Depending on the scope, a change can have far-reaching effects, and must be able to demonstrate that it’s necessary and valuable to your company, your employees and your customers. Ask yourself, is it practical to implement this change at this stage in your product lifecycle? Because it will be referenced by your team and potentially reviewed by regulators, ensure that your justification is unambiguous and to the point and includes supporting objective evidence.
-
Impact: The impact of a change could touch one or multiple areas. Let’s say that you want to change the material in a catheter device. In this case, you’ll need to conduct biocompatibility testing, review the existing manufacturing specifications, reconsider the standard operating procedures for manufacturing, and even reassess the design in relation to the change. Mapping out the impact in advance will allow you to carefully plan your change.
- Risk: Determine whether or not follow-up activities are necessary to assess the risk of your change. In-depth risk assessment may be necessary to evaluate the hazardous situations that this change could pose.
- Regulatory: Changes can, and often do, require regulatory submissions, and you want to set your expectations for this early on in your process. The person(s) in charge of regulatory affairs at your company will determine whether or not your change will require a submission to the FDA, communication with a notified body, or the equivalent methods in other target markets.
Making changes to your devices and processes should ultimately yield positive results for your business and your end users, but only when its been approached in a methodical manner and the overall impact has been assessed.
Tasks and Actions
Now that we’ve taken a look at some of the things you need to consider before implementing a change, it’s time to determine the tasks and actions necessary to set things in motion.
Consider the previous example with the proposed material change to a catheter — biocompatibility testing would be required for this change. Certain staff members would need to be tasked with overseeing the testing of the new material and with reviewing the test results. Those results would then be factored into your revised design and development plans for the catheter.
Documenting Decisions and Supporting Evidence
Throughout the entire change management process, you’ll need to document every decision that’s made regarding that change. Your documentation may include detailed explanations from your assessment of the change’s scope, impact, associated risks, tasks and actions to be taken — as well as supporting evidence to back up these claims.
This will be compiled into a change packet. Every department involved in the change will need to review and approve. With non purpose-built solutions, this can often involve a game of back-and-forth, in which one person is tasked with bringing the packet to each individual department, at which point they need to wait for it to be approved and signed before moving on.
Greenlight Guru’s QMS software has been designed to foster and streamline the change management process for medical device companies. Teams can save time with our system’s Part 11 compliant e-signatures, flexible review & approval workflows, revision control and more.
![DGCM_3]() Product Design Changes
Product Design Changes
Making changes to product design can be a complex process, so we’ve separated it into two separate categories, premarket changes and postmarket changes, each of which has its own nuances.
Pre-market Changes
A pre-market design change is implemented during product development, and perhaps while you’re still going through your design control process. At this point, you’re capturing user needs, design inputs and outputs, risk, and so on.
During design and development, you’ll be defining design outputs, which are essentially the “recipe” for your device. Everything that goes into the device, as well as the processes for manufacturing it, are included here and will form the basis for your device master record (DMR).
As you go through your premarket design and development process, you’ll be facing unforeseen obstacles, considering new opportunities, and coming up with fresh ideas and quality improvements related to your device, so some form of design change is very likely to happen during this phase.
The best practice is to document your design change decisions, but companies are often unwilling to do that for a number of reasons:
-
Concern that regulatory issues will be identified too early. Delaying potential audits or inspections for as long as possible can appeal to device developers, but a common issue here is that companies will put off design control documentation until an advanced stage in the process and end up rushing to develop their records after the fact, which often leads to things falling through the cracks.
-
Uncertainty around documentation timeline. Deciding when to document formal design controls is a common source of confusion for manufacturers. Sometimes, it may even be delayed until the verification and validation stages. However, postponing documentation can hinder progress and lead to mistakes. Companies can lose a lot of the narrative and rationale that come with more extensive design history that is started early on in product development.
And the reason many companies delay documenting design controls and design changes is that practices and procedures in place are overly complicated and overly burdensome.
To overcome this, we recommend implementing a simpler change process rooted in the practices and expectations behind design controls. One of the ways to optimize your process is to conduct a design review to document the changes to the device’s design controls and associated risks.
Design reviews act as checkpoints during your design and development process, serving as opportunities to assess your work and ensure your device meets your requirements and is being developed in a safe, effective way..
A good design change management process is flexible enough to accommodate many product development methodologies - whether that be waterfall, agile, SCRUM-agile, stage-gate, and so on.
The FDA design control waterfall, pictured below, shows the role that design reviews play in the design and development process.

Note: this image simply implies the relationship design reviews play during the design and development process and does not imply that FDA or any regulatory body requires a waterfall methodology.
Determining the timing and frequency of your design reviews will be a function of your specific device and its complexity. Design reviews are meant to shed light on potential issues related to the design and development of your device and as a decision-making process. Any design changes that have been made will benefit greatly from this type of thorough analysis.
Manufacturers should evaluate and document any issues related to a certain design change that were identified during the design review process. Conducting effective design reviews is a proven best practice for managing your design changes.
Design reviews will also help you gain insight into any additional design verification or validation that might be required before implementing your change. Design verification should prove that your design outputs meet the design inputs — i.e., the intended use of your device will be accurately produced by following your documented procedures.
Testing is often involved here. You may find that you will need to test the performance of new materials or functions described in your change. Either way, verification is mandatory with any change.
Validation, on the other hand, proves that the device you’re producing meets user needs. Additional validation is not always necessary with minor changes. However, if your change affects the way your device meets your defined user needs, you’ll need to carry out new design validation.
The documentation gained from design reviews and other design control processes will make the change management process more transparent and manageable. It will also prove to be a valuable asset to reference for any future changes that may occur after market.
Post-market Changes
Once your device reaches the market, you’ll be conducting ongoing postmarket surveillance activities, which include customer feedback and complaint management on your device. Perhaps you’re scaling your operations to mass-production, at which point you may wish to seek more cost-effective materials or processes.
Software products can also undergo post-market changes. Let’s say you’ve developed an SaMD solution intended to help detect breast cancer lesions using a locked AI algorithm. After launch, your team may identify identify enhancements to the algorithm that will assure the recommendations being given to physicians are more accurate, and this could trigger a post-market change in your software.
When making any kind of postmarket change, you’ll need to consider the impact on form, fit, and function (FFF) at this point.
Form, Fit, and Function
FFF refers to the identifying characteristics of the parts or components of your device:
-
Form refers to the shape, size, dimensions, and other visual or physical parameters of components.
-
Fit describes the way a part physically connects to or interacts with another part of your device.
-
Function refers to the action that an individual part is designed to perform.
For a postmarket change, you need to think in more granular terms to understand the impact your change might have on FFF when it comes to individual parts and their overall performance. Sometimes, a change may be trivial in these terms; other times, a single change may require additional changes to account for the impact on a device’s FFF.
For example, changing from one supplier to another requires due diligence to ensure that the new manufactured parts will be equivalent to the ones being replaced.
Remember, you should always conduct a change assessment when you’re modifying anything about a device, no matter how trivial it may seem. We recommend dedicating specific sections in your documentation to the change impact on form, fit, and function.
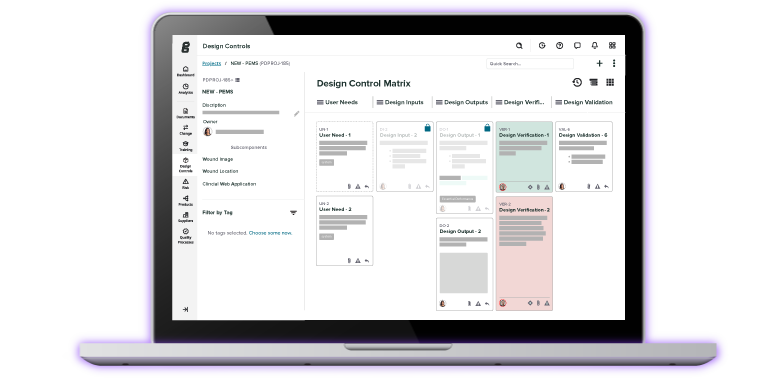
Traceability Matrix
Our recommended best practice for post-market changes involves handling your DHF as “living” throughout the entire product lifecycle and revising the product’s design control traceability matrix, as shown in Greenlight Guru’s QMS software below.

The only way to fully assess the ramifications of changes that affect FFF, risk, and verification and validation is via a traceability matrix to show the connections. If you’re making a postmarket change that affects documents recorded in the DMR, that change should be captured and documented in your design outputs.
In the past, your design history file (DHF) would typically be maintained up until the point of design transfer, but the technology has evolved since then. Unlike general purpose quality systems, the Greenlight Guru QMS allows companies to maintain a living DHF file that gets updated throughout the entire product lifecycle, even after the point of design transfer. This enables you to have more insight into the evolution of your device, with full traceability between the pre-market and post-market stages.
Design traceability allows you to gain a clear view of the specific design outputs and specifications impacted by a change, the relationship to applicable requirements or design inputs, as well as verification activities that take place.
Design validation activities are also impacted by change, and your traceability matrix allows you to explore the connections between validation and other aspects of your project development. Integrating and connecting your risk assessment in a fully traceable QMS allows you to apply a risk-based approach to product design changes.
Regulatory Impact
When you identify making a proposed change to a product that has already passed regulatory clearances / approval, you may need to complete additional regulatory documentation.
And keep in mind that in some cases, you might need to have the proper permissions from regulatory bodies before you actually implement the change. This is very important because of the impact to timeline for changes.
In the United States, devices may require a 510(k) submission, a post-market approval (PMA) supplement, or a letter to file. The FDA guidelines on change control include a decision tree to help you determine whether your change will require a 510(k) submission.
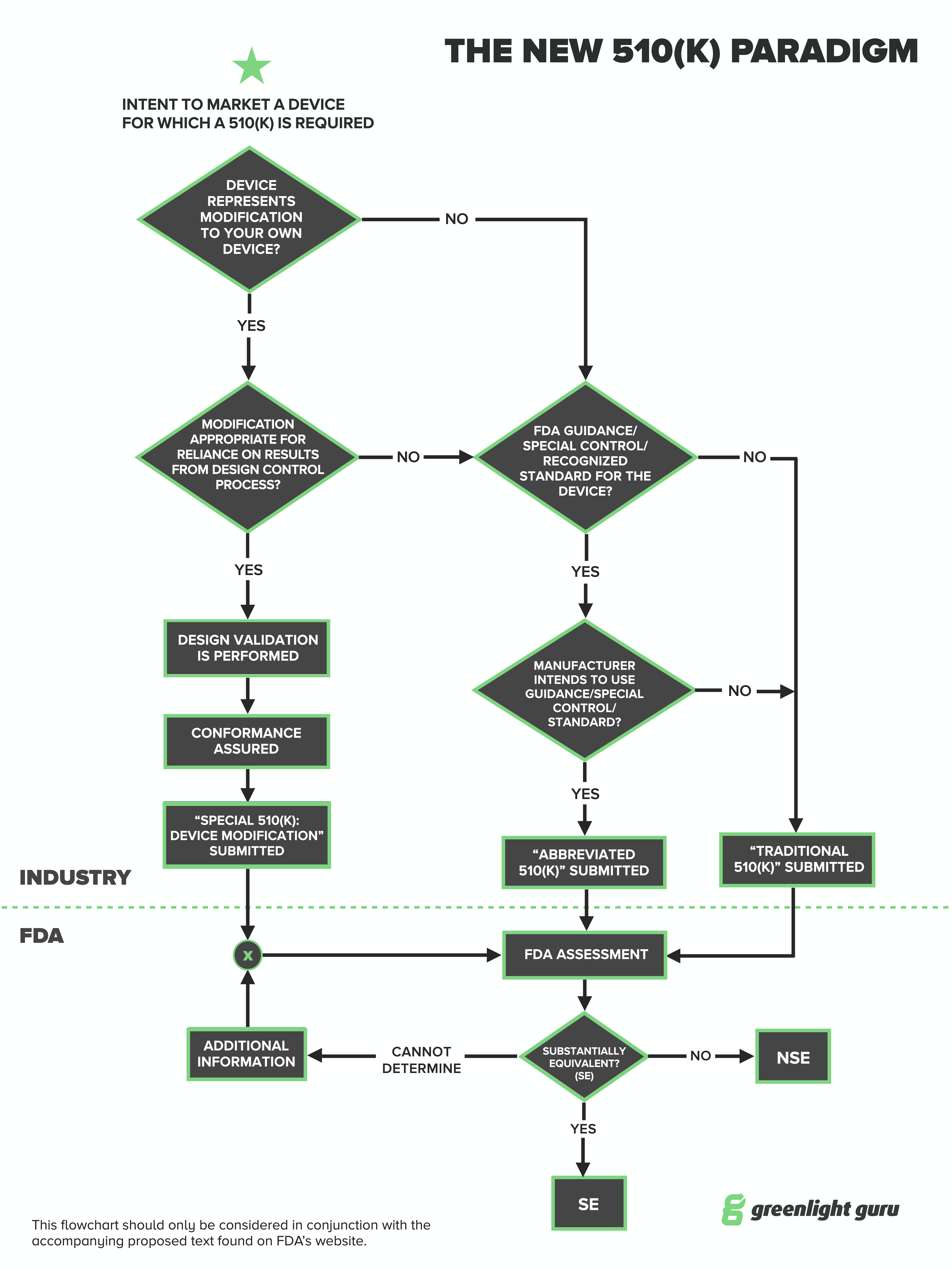
Whether you go with a 510(k), a PMA supplement, or a letter to file, you’ll be documenting your change management decisions. You’ll also be recording any testing that was done, and demonstrating your rationale and supporting evidence as to why your change is safe and compliant.
Companies that decide they don’t need to contact regulators about their change can complete and store a letter to file, an internal document which explains their reasoning.
On the other hand, a special 510(k) or a PMA supplement would be submitted to FDA, indicating your changes are “major.” Deciding between which one of the two you should submit will depend on the original regulatory pathway your device followed to get to market.
If you sell your device in the European market, you may need to notify your notified body of the proposed change prior to implementing in order to maintain your CE mark status.
These are all important factors to consider in your change management process, particularly for your post-market changes.The best practice here, regardless of your target market and relevant regulatory body, is to document your decision as part of a regulatory impact assessment.
In addition to product design changes, you should understand the process associated with any changes relating to how your device is manufactured. To make this kind of change, you’ll need to implement a manufacturing process change.
![DGCM_4]() Production Process Changes
Production Process Changes
Once you’ve had a design transfer, whether you’re manufacturing your device in-house or leveraging a third party contract manufacturer, your device master record (DMR) will be affected.
As the record of all design outputs, the manufacturing process relies heavily on this artifact. To produce the device you’ve designed accurately, manufacturers need to follow the contents of the DMR, and those contents could be subject to change for a number of reasons.
As you gain market traction, you might scale up your manufacturing process to mass production. Scaling in this way will typically involve implementing changes to manufacturing processes or materials.
To scale to mass production, you’ll need to evaluate any manufacturing process changes in terms of their impact and ability to produce the same result as before. Beyond that, you’ll often come across new suppliers or components that may have a cost or quality advantage, and the same rationale applies here.
When changing parts in a device, you will also need to update the bill of materials (BOM) in your DMR accordingly. Your BOM identifies the suppliers that provide each individual part, as well as the quantity and sometimes the cost. Any time you implement a change to existing parts, or suppliers of those parts, that change must also be updated in your BOM.
Process Risk Assessment
A best practice is to conduct a risk assessment whenever there is a manufacturing process change.
Your manufacturing partners, whether those be internal manufacturing facilities or external suppliers, should be involved during the design and development process, and this should be in motion prior to starting your verification and validation stages.
Your manufacturing process risk assessment can be handled by following the guidelines in ISO 14971, which can be broken down into four components:
-
Hazard: Potential source of harm
-
Foreseeable event: Event leading to a hazardous situation that can be easily imagined or predicted
-
Hazardous situation: A circumstance in which people, property, or the environment are exposed to one or more hazards
-
Harm: Damage to the health of people, property, or the environment.
We’ve created the Definitive Guide to ISO 14971 Risk Management that you can use to conduct an effective manufacturing process risk assessment. Your risk assessment will provide several benefits:
- It ensures that you have proper controls in place so that the product is safe for end users after you’ve implemented your change.
- It ensures that all inspection criteria and critical characteristics are thorough and diligent enough to avoid defects.
- It determines whether further steps, such as manufacturing process validation, are necessary. This would occur in the event of hazards or hazardous situations being identified as part of your new manufacturing process change, and the validation process is aimed at mitigating the risks that may emerge.
As the only QMS software on the market designed to align with ISO 14971 best practices for medical device risk management, Greenlight Guru’s Quality enables teams to conduct efficient risk assessments that can be leveraged to streamline and improve the entire change management process.
![DGCM_5]() Quality events
Quality events
The term “quality event” refers to a situation that could trigger product, process, or document changes. Quality events can and do occur sporadically throughout your product lifecycle.
Nonconformances are an example of a quality event in which a product or component fails to meet the defined quality specifications at different stages of the manufacturing process. Complaints are another example of a type of quality event that can reported by end users or partners during the feedback stages of your post-market surveillance, and this can trigger a change. Policies and procedures outlined in nonconformance management and complaint management dictate how you handle these quality events.
If a systemic issue arises, this may warrant opening a corrective and preventive action (CAPA) investigation. You may also choose to launch a CAPA investigation due to internal reviews of your products and procedures. Complaints and CAPA investigations are both forms of quality events, and there are different regulatory guidelines that apply to CAPA processes which have been published by FDA and the IMDRF.
Your CAPA investigation may necessitate a change to a process, document, or product. Greenlight Guru’s QMS software comes with built-in workflows specifically for CAPA management. If you would like to learn more, our Ultimate Guide on CAPA for Medical Devices provides a comprehensive, in-depth overview of the topic.
![change-management-software-dgcm]() Greenlight Guru Change Management Software
Greenlight Guru Change Management Software
Greenlight Guru's Quality Management software solution is designed with modern best practices that help your team streamline and control the change management process. Whether it be design changes that require updates to design controls and risk matrices, or process changes that impact a myriad of procedures, work instructions, or forms, we’ve got you covered.
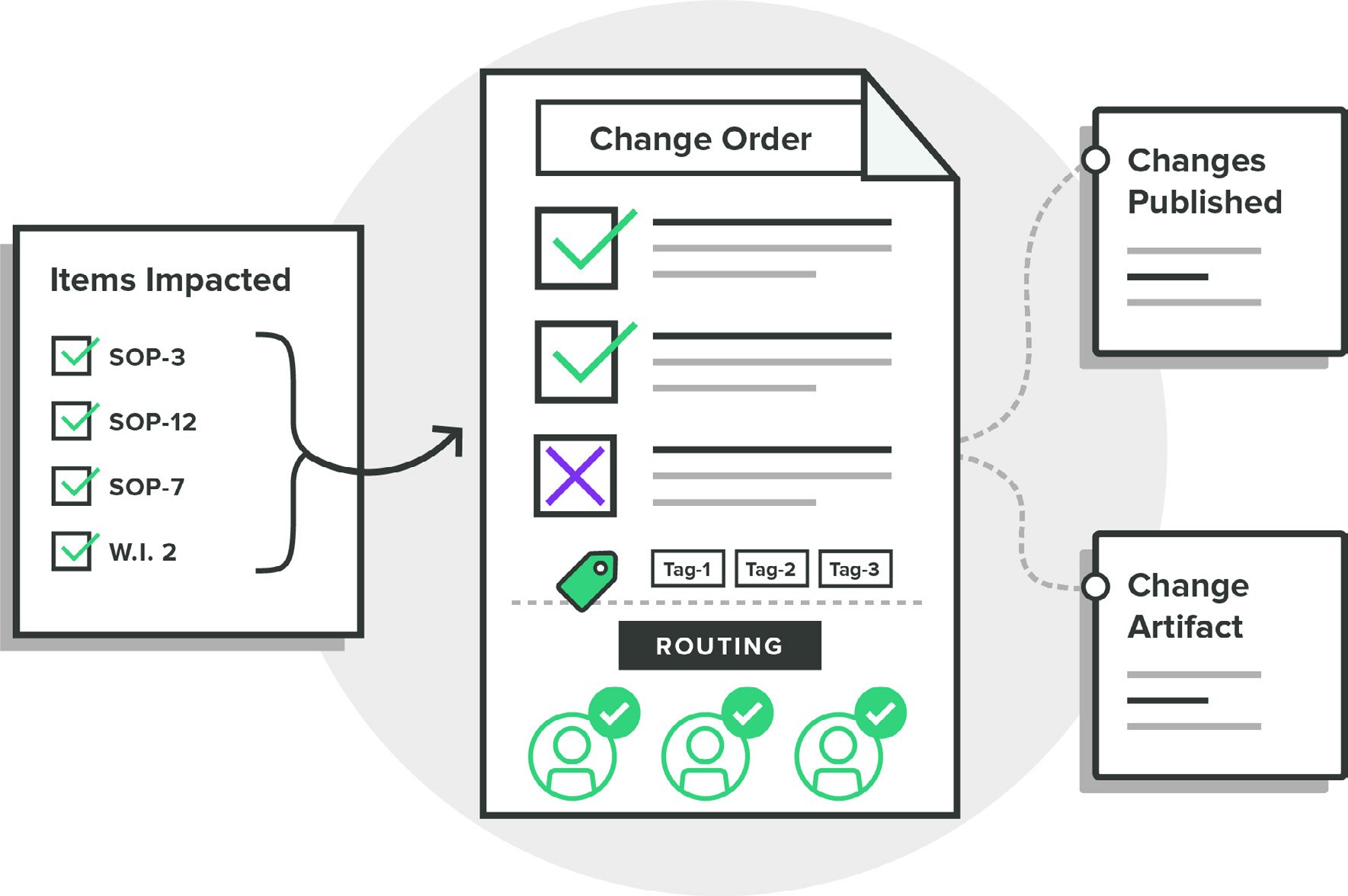
The ease with which teams can electronically review and approve changes in a Part 11 compliant manner can greatly benefit the efficiency of your pre-market design and post-market surveillance activities, as well as facilitate FDA, ISO, and EU MDR audit readiness as you continue to innovate and implement changes to your devices and processes.
With a modern, closed-loop quality system your team will have a single source of truth with full traceability between design controls, risk, documents, procedures, and quality events as changes occur.
Get your free personalized demo of Greenlight Guru →
Looking for an end-to-end solution designed to help you through each stage of the go to market process? Click here to take a quick tour of Greenlight Guru's QMS software →
Jon Speer is a medical device expert with over 20 years of industry experience. Jon knows the best medical device companies in the world use quality as an accelerator. That's why he created Greenlight Guru to help companies move beyond compliance to True Quality.
Related Posts
[VIDEO] Integrating Design Controls & Risk Management To Streamline Product Development (Make Phase)
Unannounced Audits: A Survival Guide for Quality Managers
FDA 21 CFR Part 820: 8 Most Common Mistakes to Avoid
Get your free eBook PDF
Definitive Guide to Change Management for Medical Devices
%20Definitive%20Guide%20to%20Change%20Management%20for%20Medical%20Devices_Greenlight%20Guru.png?width=250&name=(cover)%20Definitive%20Guide%20to%20Change%20Management%20for%20Medical%20Devices_Greenlight%20Guru.png)


.png)





 Controlling and Managing Change
Controlling and Managing Change Quality events
Quality events
%20Definitive%20Guide%20to%20Change%20Management%20for%20Medical%20Devices_Greenlight%20Guru.png?width=180&name=(cover)%20Definitive%20Guide%20to%20Change%20Management%20for%20Medical%20Devices_Greenlight%20Guru.png)