Understanding ISO 14971 Medical Device Risk Management

Medical device companies MUST have established risk management processes that comply with ISO 14971.
And it doesn't matter if you are developing medical devices in the U.S., EU, Canada, and so on. Every international regulatory agency you’ve ever heard of accepts ISO 14971.
ISO 14971 is a good standard. Informative and descriptive. Easy (enough) to comprehend. AND THE RISK MANAGEMENT STANDARD FOR THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY.
Let's do a brief walk-through of the standard in plain language, check out its key definitions and concepts, and break down the ISO 14971 risk management process.
FREE RESOURCE: Click here to download a free PDF of your Risk Management Plan Template.
ISO 14971 Risk Management Key & Definitions
Section 3 of ISO 14971 provides a thorough list of key terms and definitions relating to risk management. For the sake of time I am not going to go through every single term. However, I will share a few key definitions.
RISK - combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm
HAZARD - potential source of harm
HAZARDOUS SITUATION - circumstance in which people, property, or the environment are exposed to one or more hazard(s)
HARM - physical injury or damage to the health of people, or damage to property or the environment
SEVERITY - measure of the possible consequences of a hazard
RISK ANALYSIS - systematic use of available information to identify hazards and to estimate the risk
RISK ESTIMATION - process used to assign values to the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm
RISK EVALUATION - process of comparing the estimated risk against given risk criteria to determine the acceptability of the risk
RISK ASSESSMENT - overall process comprising a risk analysis and a risk evaluation
RISK CONTROL - process in which decisions are made and measures implemented by which risks are reduced to, or maintained within, specified levels
RESIDUAL RISK - risk remaining after risk control measures have been taken
Getting a grasp on the list of terms above is critical to understanding medical device risk management. These terms need to become ingrained in the lexicon of medical device professionals.
Yes, I realize you might be using other tools--such as FMEA-- to capture risk management activities. And I realize that these other tools might have similar terminology. Terms such as:
-
Failure Modes
-
Causes
-
Criticality
-
Detection
-
Risk Priority Number
It will be easy for you to fall into the trap that these other terms from your other risk tools are close enough to ISO 14971 to be more or less the same.
Please do not fall into this trap.
ISO 14971 is different from FMEA.
ISO 14971 Risk Management Process Overview
This infographic aligns with the standard directly on a one to one basis. And when you let this soak in a minute or two, you can start to see how this image can and should become the foundation for your company's internal risk management process.
(Click infographic to enlarge)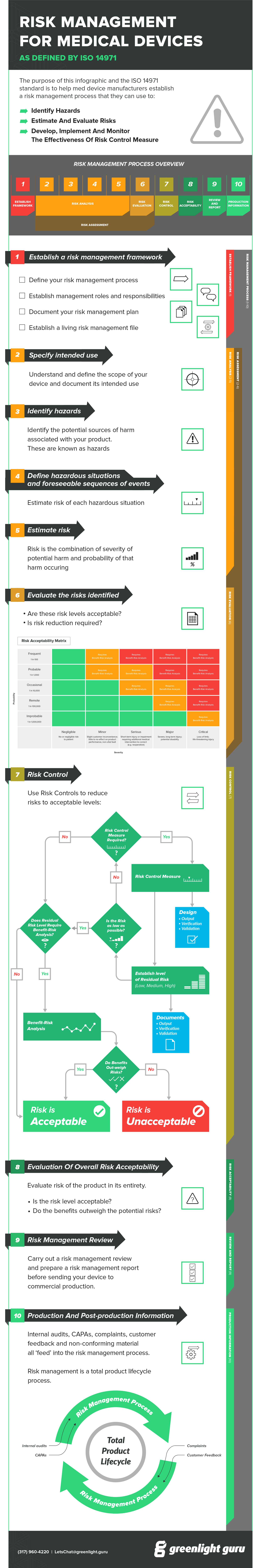
You don't have to reinvent the wheel. Nor do you need to twist and contort your current non-ISO 14971 based processes. You just need to make sure your risk management process aligns with the ISO 14971 standard.
Risk Analysis
Based on Figure 1 from ISO 14971 outlining the risk management process for medical device manufacturers, the first major phase is risk analysis.
Risk analysis is the systematic use of available information to identify hazards and to estimate the risk.
In order to do so, you need to define the scope of your medical device.
You need to specify the intended use of the product.
And then you start to identify hazards and hazardous situations. (NOTE: Refer to Annexes C in ISO 14971 for guidance on this).
Once hazards and hazardous situations are captured, you need to estimate risks.
Remember, RISK is a combination of the probability of occurrence of harm and the severity of that harm.
This can be read as:
RISK = SEVERITY (S) x OCCURRENCE (O)
However you interpret this, you need to estimate the severity of harm that can result from hazards / hazardous situations.
You then need to estimate the probability of occurrence of each harm.
Risk Evaluation
After estimating risk by defining severity and occurrence, you now need to evaluate the risks.
A very common approach for doing so is to define a risk evaluation matrix.

Simply put, this is a visual way of evaluating where your risks fall in relation to severity and probability, and can help inform which risks are acceptable and unacceptable.
That’s precisely why Greenlight Guru’s Risk Management software was built with in-line editing that makes managing and editing your Risk Matrix a simple and straightforward experience. From there, you can even configure your Risk Matrices and get ready for submissions in the way that best suits your business, all while staying compliant with ISO 14971.
Risk Control
Risk controls are implemented as a means to reduce and mitigate unacceptable risks.
There are a few options to consider when implementing risk controls.
By far the most common risk control measure is to edit product labeling. But know that labeling as a risk control is absolutely the least effective.
Ideally, risk controls should be considered according to the following priorities:
-
Product Design
-
Protective measures incorporated within the medical device
-
Labeling, instructions for use
Once implemented you need to confirm and document the effectiveness of each and every risk control measure.
Residual Risk Evaluation
After confirming effectiveness of risk controls, you then re-evaluate the resulting risks.
And if risks are still unacceptable, additional risk controls will be necessary.
Interestingly, as you implement risk controls, you could be introducing new hazards and hazardous situations.
These possible new hazards and hazardous situations also need to be estimated and evaluated.
Benefit-Risk Analysis
Sometimes additional risk controls are not practical.
In these events, you have an opportunity to conduct a benefit-risk analysis where you compare the medical benefits of your device and the residual risks.
Evaluation of Overall Residual Risk Acceptability
Evaluating risks and residual risks for individual hazards and hazardous situations is not enough.
You also need to evaluate the entire medical device and the overall residual risk acceptability.
It is possible for risks associated with individual hazards to be acceptable but that the entire product may not be acceptable.
Either way, you need to evaluate and document whether or not the product meets the acceptability criteria defined by the company.
Risk Management Review
When all the steps mentioned above have been addressed, they should be reviewed and documented as part of a risk management report.
Production & Post-Production
Medical device risk management is a total product lifecycle process.
This means you need to keep the risk management records up-to-date even after the product exits product development.
The process should involve systematic review of your risk management file and be updated when events such as complaints, product feedback, non-conformances, etc. occur.
FREE RESOURCE: Click here to download a free PDF of your Risk Management Plan Template.
Experience the new era of ISO 14971-aligned risk management with Greenlight Guru Risk Solutions
Greenlight Guru’s Risk Management software provides intuitive, purpose-built workflows to help medical device teams mitigate risk, ensure compliance, and achieve complete traceability throughout the entire device lifecycle.
→ Unlock Efficiency - Remove data silos, inefficiencies, manual efforts, and common errors by using spreadsheets or generic tools that increase costs and cause delays.
→ Enhance Collaboration - Integrate the risk management process into your entire quality management system to mitigate risk when it’s less expensive and time-consuming to do so.
→ Streamline Compliance - Purpose-built workflows to align and maintain compliance with ISO 14971:2019 and the risk-based requirements of ISO 13485:2016.
→ Integrate & Connect Risk Throughout - Easily maintain traceability between design controls and risk across the entire QMS from initial documentation through post-market surveillance.
Ready to step into a new era of risk management? Learn more and get your free demo of Greenlight Guru’s Risk Management Software ➔
Looking for a design control solution to help you bring safer medical devices to market faster with less risk? Click here to take a quick tour of Greenlight Guru's Medical Device QMS software →
Etienne Nichols is the Head of Industry Insights & Education at Greenlight Guru. As a Mechanical Engineer and Medical Device Guru, he specializes in simplifying complex ideas, teaching system integration, and connecting industry leaders. While hosting the Global Medical Device Podcast, Etienne has led over 200...
Related Posts
Can dFMEA and ISO 14971 Co-Exist in Medical Device Risk Management?
Managing Major Changes to Medical Device Packaging
What are the Risk Management Documentation Requirements of ISO 14971?
Get your free template
Risk Management Plan Template







